Sony Interactive Entertainment has patented an adaptive controller featuring virtual, customizable buttons on a fully touch-sensitive surface, according to Insider Gaming. The patent, dated 27 January 2026, describes a revolutionary gamepad design that could address the limitations of traditional fixed button layouts.
The proposed controller would support gestures such as taps and swipes whilst dynamically adapting control zones to finger positions. Sony cites difficulties with fixed layouts as a key problem, particularly for users who find current controllers too large or too small.
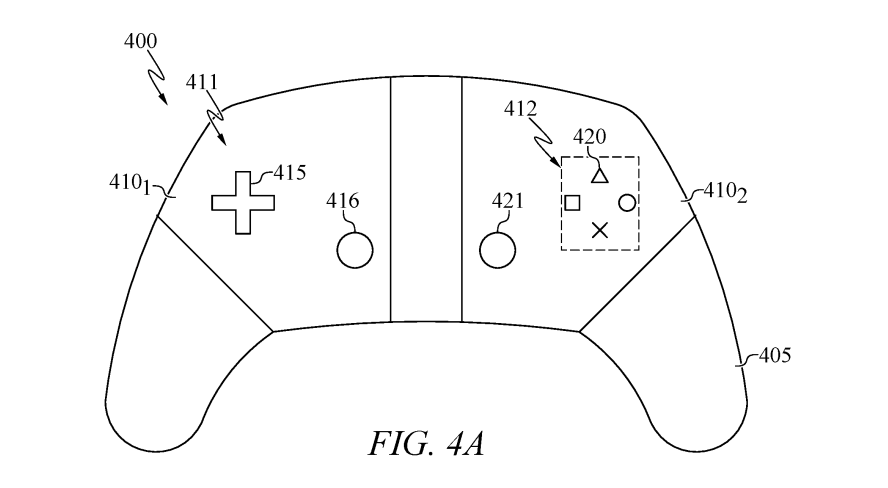
How the adaptive controller works
According to the patent documentation, Sony's adaptive controller replaces physical buttons with a digital screen that allows complete customisation of control layouts. The touch-sensitive surface can recognise different input methods, from simple taps to complex swipe gestures.
The patent drawings show various button and D-pad placements that users could configure based on their preferences or specific game requirements. This approach would theoretically allow for unlimited control schemes, adapting to different hand sizes and gaming styles.
"Sony has registered a patent for an unusual gamepad without physical buttons. It features a fully touch-sensitive surface that supports gestures such as taps and swipes, and it will be able to adapt to finger positions, dynamically changing the control zones," Gaming.Bo3.gg noted on social media.
Sony's controller innovation history
This patent continues Sony's track record of controller innovation spanning multiple console generations. The company pioneered the twin analogue stick layout with the original DualShock controller for PlayStation, establishing what became the industry standard.
Subsequent innovations included Sixaxis motion-sensing technology in the PlayStation 3 controller, the PS4's integrated touchpad, and the PlayStation 5's haptic feedback and adaptive triggers. Each generation has introduced new ways for players to interact with games.
The adaptive controller patent suggests Sony continues exploring ways to enhance player control and accessibility, potentially addressing the needs of gamers who struggle with traditional controller layouts.
Patent doesn't guarantee product
Patents indicate future considerations rather than guaranteed product releases. Sony regularly files patents for various technologies that may never reach commercial production. The adaptive controller design, whilst innovative, faces practical challenges including battery life, manufacturing costs, and player acceptance.
The gaming industry has seen mixed reactions to revolutionary controller changes. Whilst some innovations like analogue sticks became universal, others like motion controls found more limited adoption. A fully virtual button layout would represent a significant departure from established gaming conventions.
The rise of mobile gaming has familiarised younger players with virtual controls, potentially easing adoption of such technology. However, many gamers prefer the tactile feedback of physical buttons for precision gaming.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Sony's new controller patent?
Sony has patented an adaptive controller featuring a fully touch-sensitive surface with virtual, customizable button layouts and gesture support. The patent was filed on 27 January 2026.
When was the Sony adaptive controller patent filed?
The patent for Sony's adaptive controller was dated 27 January 2026, according to the official documentation.
Will Sony release a controller based on this patent?
There is no official confirmation that a product based on this patent will be released. Patents indicate future considerations rather than guaranteed products.
How would virtual buttons work on a controller?
The patented design features a digital screen surface that can display customizable button layouts. It recognises various inputs including taps and swipes whilst adapting to finger positions.
What problems does this controller solve?
Sony's patent addresses fixed button layout limitations, particularly for users who find current controllers too large or too small, and allows for personalised control schemes.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest updates and news
















Member discussion